Insurable interest insures against the prospect of a loss to this person or entity. Insurable interest insures against the prospect of a loss to this person or entity.

Insurable Interest – Law Of Insurance – Article Highligjts Importance Of Insurable Interest In Law – Studocu
For example, a corporation may have an insurable interest in the chief executive officer (ceo), and an american football team may have an insurable interest in a star, franchise quarterback.

Insurable interest definition and example. Without insurable interest, there is no basis for an insurance policy. A person has an insurable interest in the life of another where there is a reasonable probability that he will gain by the latter’s remaining alive or lose by his death. A person is expected to have reasonable interest in a longer life for himself, his family, business and hence is in need of acquiring insurance for these.
That is, when the insured property/person is affected by a. Normally, insurable interest is established by ownership,. Thus, a person has an insurable interest in their own life, their family, their property, and their business.
They have insurable interest to the extent of their part or financial interest. Insurable interest is a collection of risk exposure, to protect policyholders from financial losses. In fact, before the promulgation of certain acts by english parliament, it was not.
Insurable interest is an investment with the intent to protect the purchaser from financial loss. It means that the proposer of insurance must have financial interest in the property/person insured. If a storm knocks over a tree which damages both your car and your neighbor’s, you would have insurable interest in your vehicle but not your neighbor’s.
For example, a corporation may have an insurable interest in the. Therefore, entities who would not suffer a financial loss. Insurable interest is almost a legal right to insure.
That right of property which may be the subject of. More definitions of insurable interest insurable interest means any actual , lawful , and substantial economic interest in the safety or preservation of the subject of the insurance free from loss , destruction , or pecuniary damage or impairment. Insurable interest refers to the reasonable concern to secure insurance to protect against some form of loss.
Part owners or joint owners: Types of insurable interest are fidelity guarantee insurance, credit. Insurable interest is defined as the reasonable concern of a person to obtain insurance for any individual or property against unforeseen events such as death, losses, etc.
In auto insurance, the most obvious example of insurable interest is the auto itself on a full coverage policy. Examples of insurable interest which exist in the following cases: For example, it is life in life insurance, factory, machinery, stock, house, building, etc.
Insurable interest is the basis of all insurance policies. This interest is called insurable interest. Insurable interest is a person’s legally recognised relationship to the subject matter of insurance that gives them the right to effect insurance on it.
What is insurable interest example? A person has such an interest in property or in the life of a person if damage or destruction of the property or death of the person would expose him to pecuniary loss or liability. You have to first prove the insurable interest.
Insurable interest is the first and foremost principle in insurance parlance. To exercise insurable interest, the policyholder would buy insurance on the person or. Section 5(2) of marine insurance act 1906 states that person has an insurable interest who benefits safety or due arrival of the property or.
A person has an insurable interest in something when loss of or damage to that thing would cause the person to suffer a financial or other kind of loss. Any person, item, event, or action can have insurable interest if its loss or damage results in a financial burden. Simply put, insurable interest means that the beneficiary, or person benefitting from the proceeds of the insurance policy, has a financial tie to the insured person.
If you can’t prove the insurable interest then the insurance company won’t allow you to buy an insurance policy. Definition, types, and example (explained) you can’t just buy an insurance policy for yourself or someone who is dependent on you. Owners have got insurable interest to the extent of full value.
In order to affect a valid insurance a person must prove some kind of interest in the life sought to be insured. An insurable interest is an object which, if damaged or destroyed, would result in financial hardship for the policyholder. Mortgagor, being the owner of the property, has got insurable interest.
It is a fundamental prerequisite for any insurance policy. Insurable interest exists when an insured person derives a financial or other kind of benefit from the continuous existence, without repairment or damage, of the insured object.

Insurable Interest Definition Types Example Explained

Insurable Interest Definition Types Example Explained

Essentials Of Insurable Interest – Qs Study

Insurable Interest Case Study Free Essay Example
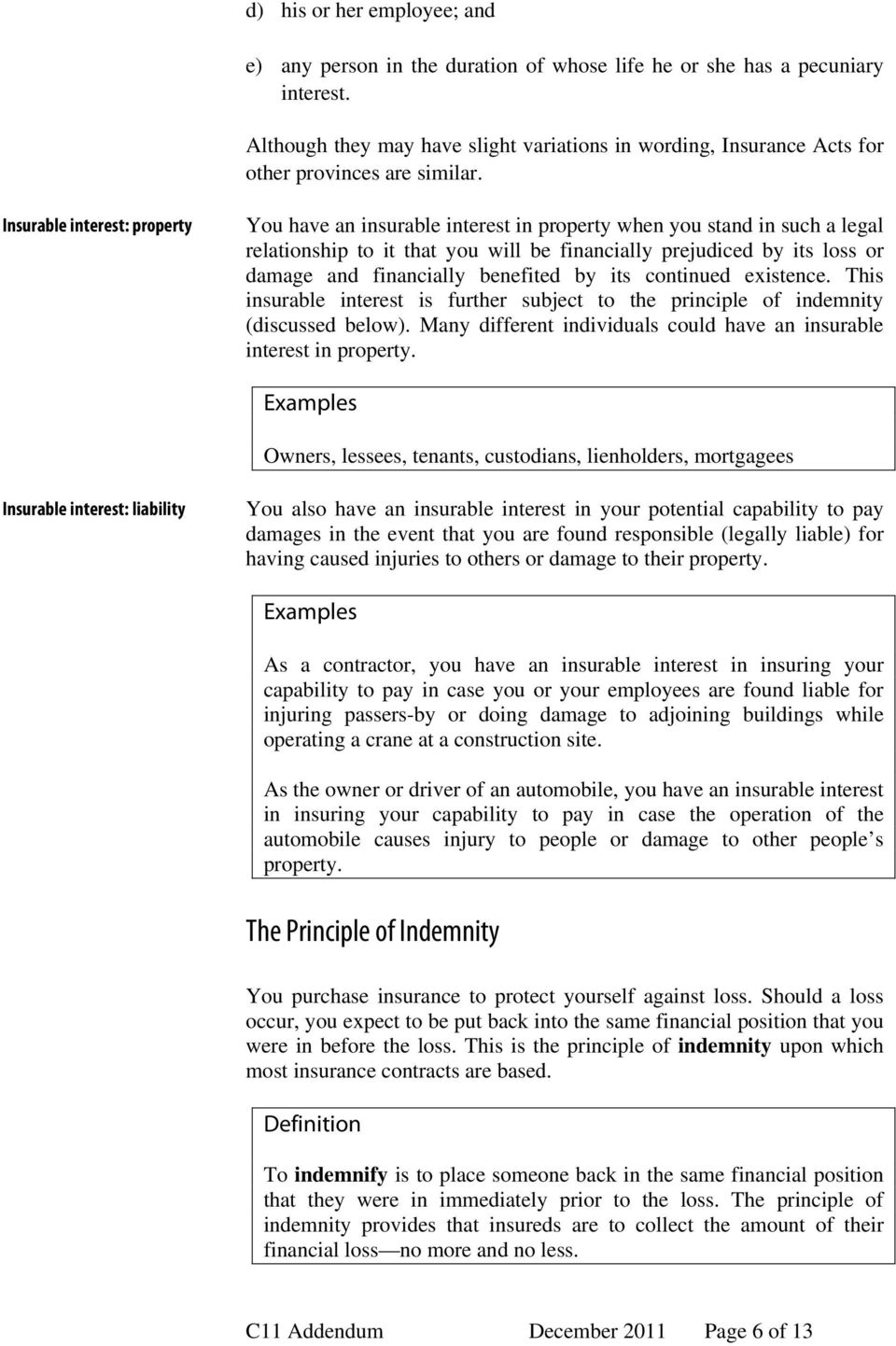
C11 Principles And Practice Of Insurance – Pdf Free Download

The Doctrine Of Insurable Interest Meaning And Case Laws – Strictlylegal

Insurable Interest Definition Types Example Explained

What Is The Principle Of Insurable Interest

Insurable Interest Definition Types Example Explained
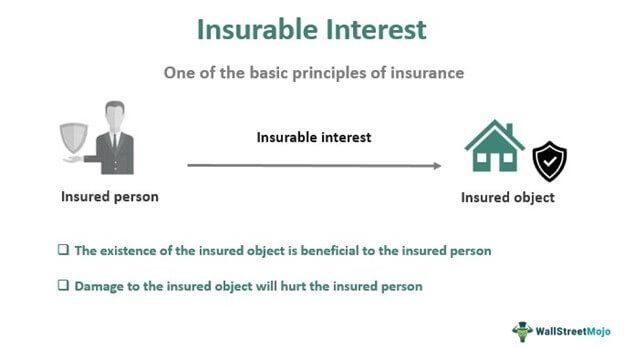
Insurable Interest – Meaning Principle Example How It Works

Requirement Of Insurable Interest For Life Insurance
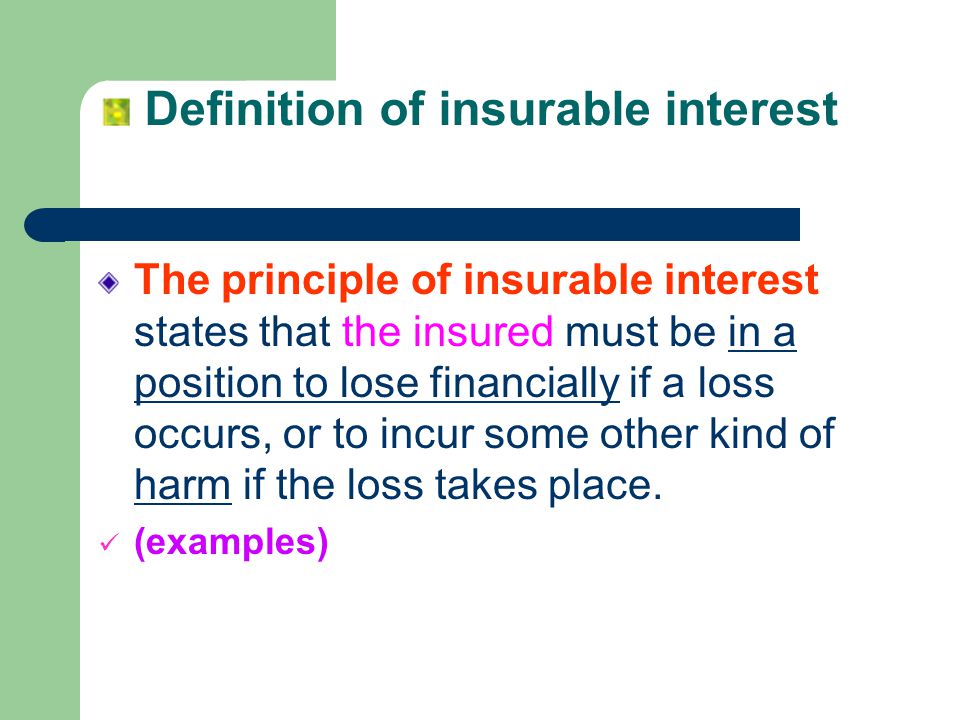
Fundamental Principles In Insurance – Ppt Video Online Download

Part 5 – Introduction To Insurance – Insurable Interest – Youtube








/types-of-insurance-policies-you-need-1289675-Final-6f1548b2756741f6944757e8990c7258.png)





